Overview
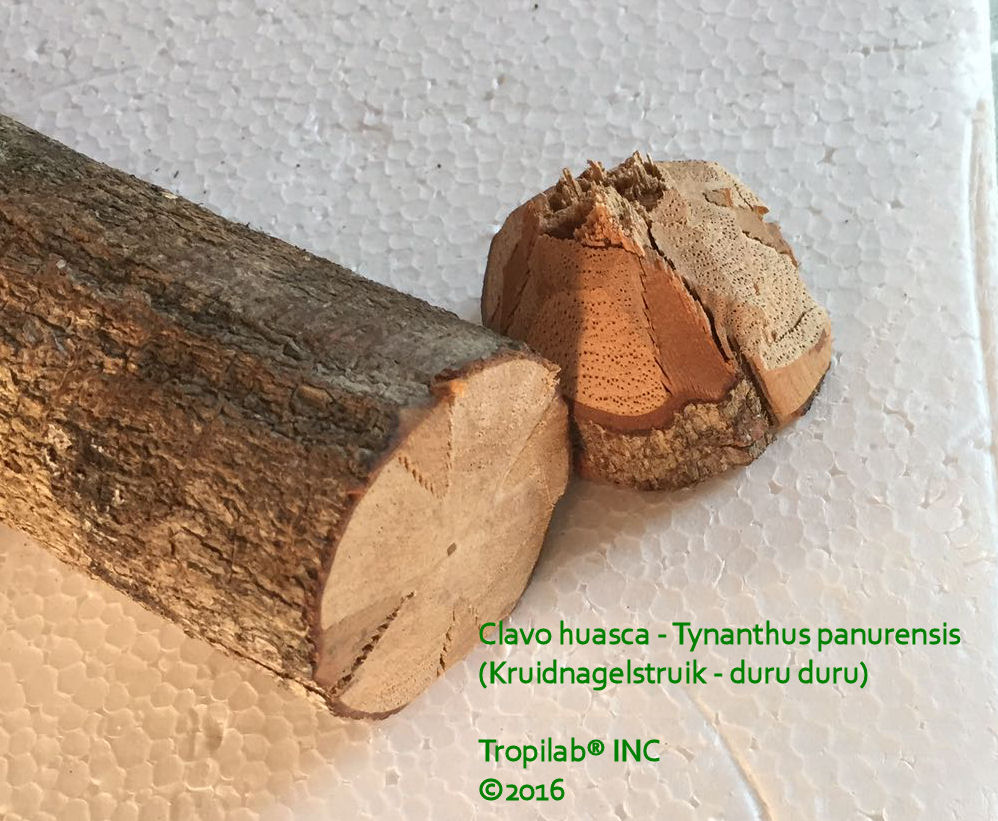
 Clavo huasca (Clove vine or White clove) is a large woody vine (liana) from the
Amazon rainforest.
Clavo huasca (Clove vine or White clove) is a large woody vine (liana) from the
Amazon rainforest.
The bark and root have a typically clove-like smell. The vine has a distinctive "Maltese cross" design in
the wood, when cross-sectioned.
It is an adequate exotic aphrodisiac (natural sexual stimulant) and used by both men and women for sexual potency and
erections.
Also used as a digestive aid, general tonic, a remedy for rheumatism and as an appetite stimulant; it also helps with
toothache.
Constituents
Alkaloid D-tubocurarine, mono- and bisindole quaternary alkaloids: Guiaflavine, 5',6'-dehydroguiaflavine,
9-methoxy-Nb-methylgeissoschizol; C-alkaloid O, fluorocurine, mavacurine, macusine B and C-profluorocurine,
phenylpropanoid glycoside (eugenol), katchimoside.
Pharmacology
 Clove vine is used in Traditional Amazonian Medicine as a tonic and energizer as well as a remedy for rheumatism.
Clove vine is used in Traditional Amazonian Medicine as a tonic and energizer as well as a remedy for rheumatism.
A study of the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Clove vine bark extract, showed the presence
of saponins and a high concentration of phenols and flavonoids.
Tests also showed that the extract has free radical-scavenging antioxidant properties and reduces microsomal
lipid peroxidation, uric acid synthesis, and tumor necrosis factor-α production.
The bark extract (as an herbal tincture) could be beneficial as a remedy for inflammation (the main traditional use of
this plant).
It is also regarded as a very good remedy for dyspepsia and difficult digestion.
 Dosage
Dosage
Tincture: 2 - 5 ml; 30 minutes before having intercourse.
Infusion (herbal tea): half - cup daily. 30 minutes before sexual intercourse.
Side effects
No adverse side effects are known
Reference
Anesthesia before and after curare.
Foldes, F.F.
Anasthesieabteilung des Albert-Einstein-College of Medicine.
Anaesthesiol Reanim, 1993, 18(5):128-31. (retrieved June 20 2005) James, Mel. Harold Griffith, Heirloom Series, Volume 6.
(retrieved June 20 2005)
"Curare", Blue Planet Biomes, 2000. (retrieved September 27 2005)
Bioactive properties of Tynanthus panurensis (Bureau) Sanwith bark extract, the Amazonian "clavo huasca".
Morales L, Acero N, Galán A, Perez-García C, Alguacil LF, Muñoz-Mingarro D.
Bisindole alkaloids from Strychnos guianensis are effective antagonists of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in cultured
human TE671 cells.
Wins P, Margineanu I, Penelle J, Angenot L, Grisar T, Bettendorff L.
Center for Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, University of Liege, place Delcour, 17, 4020 Liege, Belgium
Quaternary indole alkaloids from the stem bark of Strychnos guianensis.
Penelle J, Tits M, Christen P, Molgo J, Brandt V, Frederich M, Angenot L.
Universite de Liege, Institut de Pharmacie, CHU, Belgium. jacques.penelle@ulg.ac.be
The above presentation is for informational and educational purposes only.
It is based on scientific studies (human, animal, or in vitro), clinical experience, or traditional usage.
For many of the conditions discussed, treatment with prescribed (RX) or over - the - counter medication (OTC) is also
available.
Consult your doctor, practitioner, and/or pharmacist for any health problem and before using dietary supplements or
before making any changes in prescribed medications.
|

